

Overview
Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) is a four-year program consisting of general education, major and professional nursing courses. The professional courses are embedded from the first to the fourth year with emphasis on nursing concepts with corresponding related learning experiences (RLEs). The BSN program provides an intensive nursing practicum that will refine further the nursing competencies to ensure achievement of the BSN program outcomes required of an entry level nurse.
BSN was first recognized by the Department of Education in June 9, 1958 as a three-year diploma program leading to a non-degree Graduate in Nursing (GN) certification. A two-year supplemental advanced professional post-graduate program was soon offered to provide opportunity for GN program graduates to broaden their knowledge, appreciation and understanding of clinical teaching and public health nursing.

In June 1961, the five-year straight baccalaureate program leading to the degree Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) was established. The following year, a supplemental BSN program for graduate nurses began. The last batch of the GN program graduated in 1964 while its supplemental program was terminated in 1976, the same year that the baccalaureate program became a four-year program.
In 1984, the BSN curriculum was revised into a competency based, community-oriented curriculum. Five years later, the BSN program was mandated as the sole program intended as the academic preparation of nursing professionals, a milestone in nursing education.
The BSN program has undergone several revisions and changes since then, adhering with changing government policies and meeting the shifting industry standards of the nursing profession. One of these curricular revisions occurred in 1998 under CHED memorandum order no. 27, series of 1998, which required students to undertake the Associate in Health Science Education (AHSE), a two-year certification program with an option to continue to the full BSN program.
In 2006, the university established the In-house Nursing Review Program for BSN graduates, which ran for three years until it was integrated into the curriculum as part of the Nursing Competency Appraisal in 2009. Around this time, the institute began to optimize and utilize technologies for e-learning such as video discussions, demonstrations and examinations in addition to traditional classroom teaching. This included the Virtual Integrated Nursing Education Simulation (VINES) Laboratory, where students can practice their skills through human patient simulators and other state-of-the art equipment in a realistic hospital setting. The program also established linkages with hospitals and clinic affiliations across Metro Manila and the provinces of Bulacan, Cavite, and Batangas.

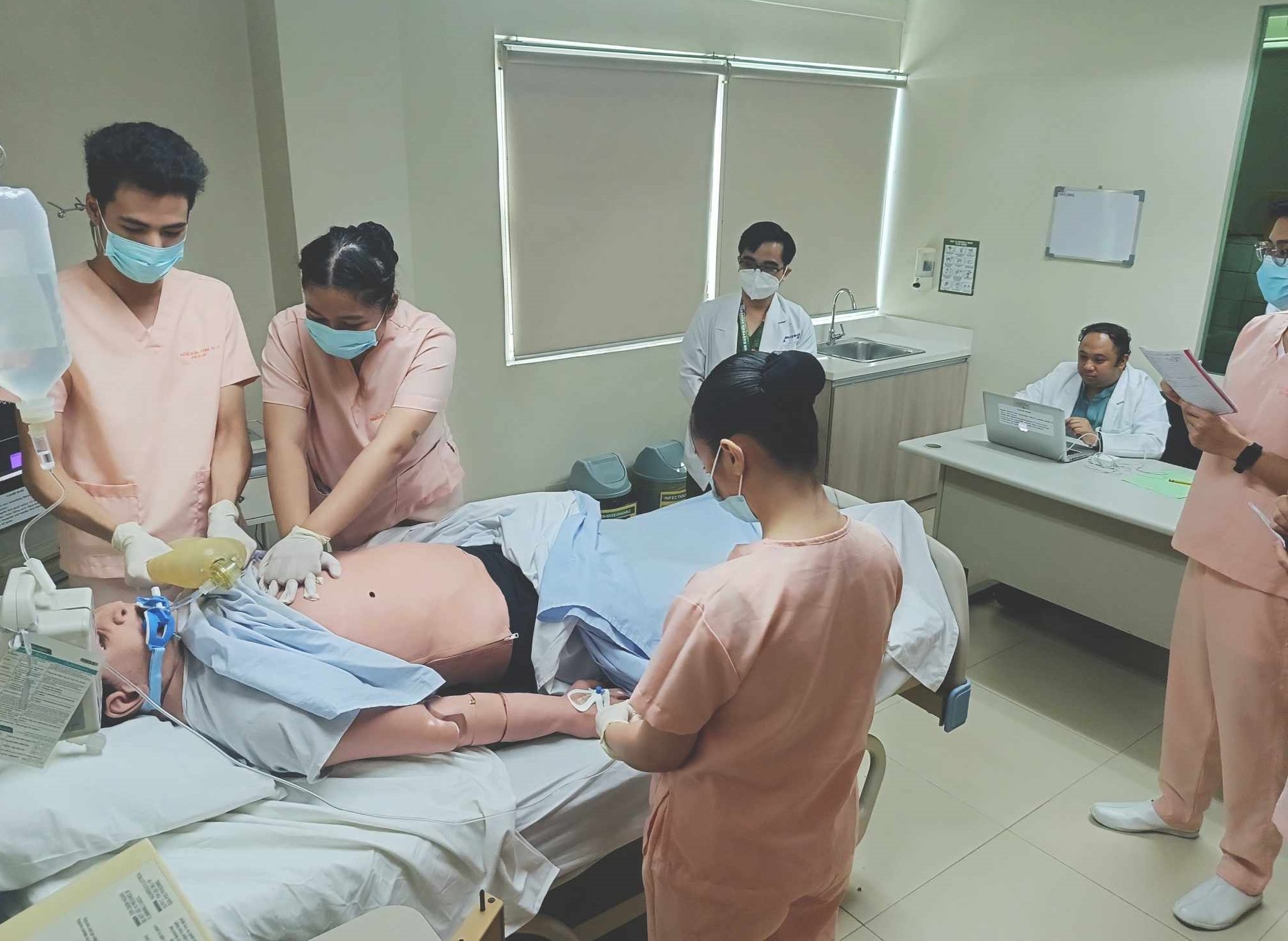
Another BSN program revision occurred in 2008 following the issuance of CMO no. 05, s. 2008, which abolished the AHSE program and allowed students to take some professional courses as early as during their first year in the program. The CHED also proposed a new curriculum for AY 2009 to 2010. This also marked the shift towards utilizing the Nursing Online platform and the practice of evidence-based nursing.
In 2011, the program started promoting a research culture among its faculty and students and establishing international partnerships and linkages, such as with Anhui and Taishan Universities in China. Curriculum changes began again following the implementation of the K-12 basic education program and the country’s paradigm shift from competency-based to outcomes-based education.
Presently, BSN has achieved Level III accreditation status under the Philippine Accrediting Association of Schools, Colleges and Universities (PAASCU) valid until November 2021. The program is currently working to achieve Level IV accreditation status as it strives to create and shape globally competitive nurse leaders.

BSN graduates belong to Level VI (Baccalaureate) of the Philippine Qualifications Framework (PQF) under qualification code number 60913 and are also recognized under the ASEAN Qualifications Reference Framework (AQRF). They are also qualified to take the Philippine Nursing Licensure Examination (PNLE) under the Professional Regulation Commission (PRC), along with any other certification assessments for global professional practice in the nursing field. Graduates may also opt to pursue post-graduate degrees or take the National Medical Admission Test (NMAT) to pursue a degree in medicine.